Is Myopathy Curable? Our Neurology Specialist Answers the Basic Questions
This article on myopathy is an updated version that was originally published in November 2018. It contains the latest information and developments as of February 2024.
If you have a muscle disease, you may have myopathy. This is a medical term that means your muscles are not working properly. Some of the common signs of myopathy are muscle weakness, pain, cramps, stiffness, and fatigue. Myopathy can have different causes, such as genetic mutations, infections, inflammation, toxins, or drugs. Some types of this condition are mild and do not affect your daily activities, while others are severe and can lead to disability or death. That is why it is important to see a neurologist like Dr. Sarbjot Dulai, who specializes in diagnosing and treating muscle disorders in the Northern Virginia area. He can help you find the cause of your myopathy and offer you the best options for managing your condition and improving your quality of life.
What You Need to Know About This Muscle Disorder
Myopathy is a term that refers to any disorder that affects the skeletal muscles, which are the muscles that enable movement and posture. There can be different causes, symptoms, and treatments depending on the specific type and severity of the condition.
Some Common Forms of Myopathy
Myopathy can result from genetic mutations, hormonal imbalances, immune system attacks, or exposure to harmful substances. Some of the common forms of myopathy are:
- Inherited myopathies: passed down from parents to children through defective genes. Some examples are Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy, which are caused by a lack of a protein called dystrophin that helps maintain muscle strength and structure.
- Endocrine: related to problems with the endocrine system, which is the network of glands that produce and regulate hormones. Some examples are hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, which are caused by too little or too much thyroid hormone, respectively.
- Inflammatory: caused by inflammation of the muscle tissue due to an abnormal immune response. Some examples are polymyositis and dermatomyositis, which are characterized by muscle pain, weakness, and skin rashes.
- Toxic: caused by exposure to certain chemicals or drugs that damage the muscle cells. Some examples are statin-induced myopathy, which is caused by a type of medication that lowers cholesterol levels, and alcoholic myopathy, which is caused by chronic alcohol abuse.
How This Disease Affects Your Muscles
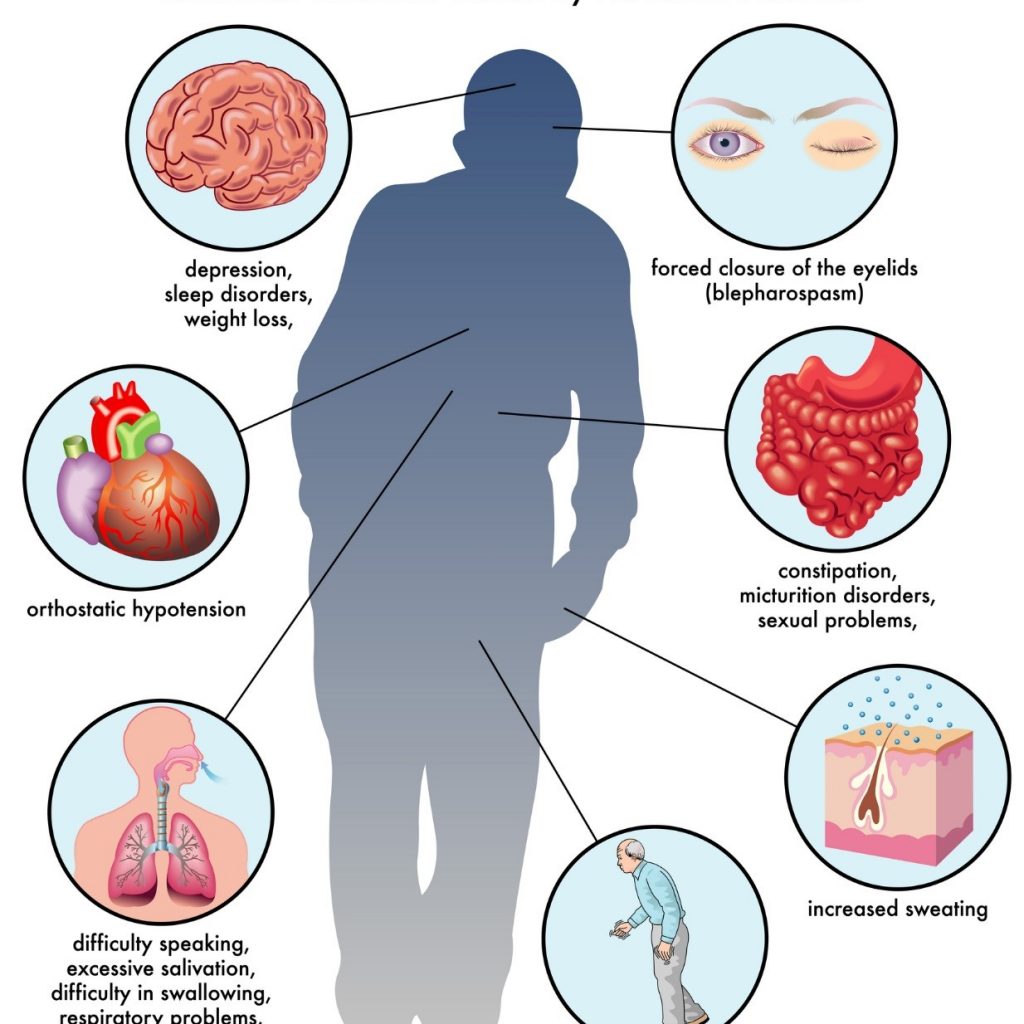
As there are more than 600 muscles in the human body, myopathy can have different causes and affect different areas. Here are some common signs and symptoms of myopathy that you should be aware of:
- Weakness in the upper arms, pelvis, shoulders, and thighs. This is usually the first sign of myopathy and can make it hard to lift objects, climb stairs, or get up from a chair.
- Cramps, tenderness, pain, aching, stiffness, and tightness in the muscles. These can occur during rest or after exercise and can interfere with your daily activities and sleep quality.
- Involvement of the hands and feet. This can happen in more advanced stages of myopathy and can affect your fine motor skills, such as writing, typing, or buttoning clothes.
- Difficulty breathing, swallowing, or speaking. This can happen if the muscles of the chest, throat, or tongue are affected by myopathy. It can lead to serious complications such as pneumonia or choking.
How Myopathy Is Diagnosed and Treated
If you suspect that you have a muscle disorder, you should consult your doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Your doctor may perform a physical examination and ask you about your medical history, family history, and symptoms. Your doctor may also order some tests to confirm the diagnosis and identify the cause of your myopathy. Some of these tests may include blood tests, urine tests, muscle biopsy, electromyography (EMG), or genetic testing.
The treatment of myopathy depends on the type and cause of the condition. Some forms of myopathy may be treated with medication, such as anti-inflammatory drugs, hormone replacement therapy, or immunosuppressants. Some forms of myopathy may require physical therapy, occupational therapy, or speech therapy to improve muscle function and quality of life. Some forms of myopathy may need surgery to correct structural problems or implant devices such as pacemakers or ventilators. Some forms of myopathy may not have a cure but can be managed with supportive care and lifestyle changes.
Since this is a chronic condition, it will require ongoing management and care. The treatment options depend on the specific type and severity of your myopathy. They may include:
- Medications to suppress the immune system, reduce inflammation, or treat underlying conditions that cause myopathy.
- Physical and occupational therapy to improve your muscle strength, mobility, and function.
- Dietary management to ensure adequate nutrition and prevent weight loss or gain.
- Cardiology consultation to monitor and treat any heart problems that may arise from myopathy.
- Surgery to correct any deformities or contractures that may develop in your limbs or spine due to myopathy.
Myopathy is a serious condition that can affect your muscles and your overall health. If you have any concerns about your muscle health, you should seek medical attention as soon as possible.
If you experience any muscle related issues and have access to Leesburg, Virginia contact Dr. Sarbjot Dulai at Neurology Associates. He is an expert in diagnosing and treating myopathy and other neuromuscular disorders. He will perform a thorough evaluation of your medical history, physical examination, and neurological tests to determine the cause and type of your myopathy. He may also order laboratory tests, imaging studies, muscle biopsies, or genetic tests to confirm the diagnosis.
Resources:
Mt. Sinai – https://www.mountsinai.org/care/neurology/services/neuromuscular-disease/conditions/myopathy
Penn Medicine – https://www.pennmedicine.org/for-patients-and-visitors/patient-information/conditions-treated-a-to-z/myopathies